We have all received a phishing email at some point in our lives. According to a 2022 study, scams accounted for 47 percent of spear-phishing attacks globally, making them the predominant form of cyber attack within this category. In this article, you will find 15 useful tips to protect yourself from such cyberattacks.
How hackers operate
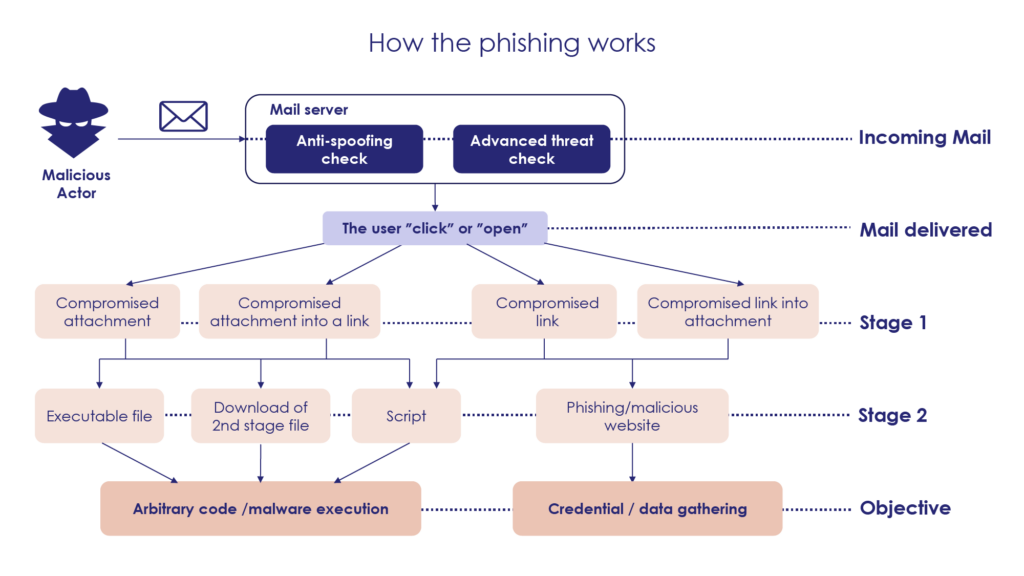
Most phishing techniques follow the same pattern:
Step 1: Getting those clicks
The hacker needs to convince the email recipient that they are a legitimate sender. They often accomplish this by spoofing an email address or by impersonating legitimate domains. Some hackers collect information about their intended target to forge a familiar-looking email.
Step 2: Bypassing protection
The hacker’s objective is for their target to open the malicious attachment or link. To bypass basic malware protection, hackers often hide malicious code in a file that is not supposed to be an EXE file (like a macro in a document or code in a PDF). Most malicious codes or links are well hidden in emails.
Step 3: Executing the malicious code or gathering information
It takes hackers several steps to develop a malicious code or link. First, they create a code that appears safe in order to bypass malware protection: this is the link or file that is displayed when the email is opened. However, there often an additional link or file within this code which upon activation executes a malicious code. This second link or file has not been seen or verified by mailbox protection since it is hidden within the first code.
Step 4: Compromising the account
Once a malicious code has been activated, the recipient’s account has been compromised. This may lead to extortion, theft of confidential information, encryption of the recipient’s data, etc.
How to protect yourself
Anti-spoofing protection
Because it’s better to be safe than sorry, we advise you to enable and configure the three most popular types of anti-spoofing protection.
Tip n°1: Enable DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). This is an email authentication method that validates the cryptographic signature in email headers. DKIM verifies sender domain authenticity and guarantees the message’s integrity.
Tip n°2: Implement Sender Policy Framework (SPF). This anti-spoofing method is particularly useful since it determines whether an IP address is permitted to send emails on behalf of the assumed domain name.
Tip n°3: Deploy Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC). This email validation system relies on SPF and DKIM analyses as well as other checks, and carries out the appropriate action on a case-by-case basis.
It is important to keep in mind that anti-spoofing solutions will never be able to protect you from certain spoofing techniques, such as sending an email from a look-alike domain name (i.e., amarls.com instead of amaris.com).
Advanced configurations and dedicated tools
Another way to protect yourself from hackers and spam is to configure email filters and install anti-spam tools.
Tip n°4: Identify the most dangerous attachment types (.exe, .php., etc.) and set the mail server to block these types of files by default.
Tip n°5: Use a sandbox filter to test links and attachments before it enters the user’s mailbox.
Tip n°6: Install an anti-spam tool that can verify the reputation of the sender and set up rules for advanced email content filtering (like YARA rules).You can also add an email banner which will remind users to exercise caution when handling links or attachments from external contacts.
These filters and tools should shield users from receiving malicious emails in their inbox.
User training
This is the very last barrier before a user opens the infected link or attachment. User awareness is crucial to preventing cybercrime.
Tip n°7: Conduct phishing awareness training at least once a year: teach users how to recognize hacking attempts.
Tip n°8: Get everyone to act as a Human Firewall by being Responsible for Security. Learn more about Human Firewall in this article.
Tip n°9: Implement an easy and simple company-wide incident reporting process so users can immediately report any suspicious emails. Including a ‘report’ button in your mailbox may also be appropriate.
As cybercrime protection evolves, so will hackers’ tools: your people need to be prepared and properly trained to be able to spot cyberattacks.
But what if we click?
Fortunately, there are still defenses that can be put in place to prevent and reduce data breaches and compromised devices.
Endpoint protection
Once an infected file or attachment has been opened, only malware protection can intercept the malicious software from corrupting the user endpoint.
Tip n°10: Install an antivirus to protect users from common types of malware and malicious scripts.
Tip n°11: Install an Endpoint Detection and Response (EDRE) to analyze the behavior of a program and to trigger an alert if it matches particular patterns.
Tip n°12: Make sure that the passwords for the local administrator account are different on each computer of your network. Or better still, if you don’t need them: disable the administrator account and debugging privileges to limit the effects of malware.
Tip n°13: Utilize web browser extensions for phishing detection. Consider employing web browser extensions specifically designed to identify and alert you about potential phishing websites. These extensions analyze the website’s content, links, and other characteristics to assess its legitimacy. If a website raises suspicion, the extension will notify you, preventing you from inadvertently entering sensitive information. Several reputable extensions are available, such as MalwareBytes Browser Guard or BitDefender TrafficLight.
Credential protection
Some hackers set up phishing websites to obtain users’ credentials (login/password). However, even if these credentials are stolen, there are still ways to mitigate further damage.
Tip n°14: Enable Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) for all sensitive or important web applications. MFA requires an additional identity verification prior to account access, like requesting the user to provide a code which has been sent to the account holder’s phone.
Tip n°15: Leverage password managers for phishing defense. Password managers offer an additional layer of protection against phishing attacks by preventing auto-filling of login credentials on illegitimate websites. These tools store your passwords securely and can identify phishing websites by comparing them against a database of known malicious websites. If you attempt to log in to a website that is flagged as suspicious, the password manager will warn you and prevent the auto-fill of your credentials.
Today, most cyber insurance companies will request MFA to be enabled. Insurance prices may rise for businesses that have not installed this authentication mechanism.
Do you want to find out if your company is vulnerable to phishing? Learn more about our custom-made Cyberscurity offer here!


